This pic doesn't look quite right, at top of right palm tree trunk.
Will the 68K and Z80 emulators both contain PSRAM code? If so, a single PSRAM cog would appear to be better so that spare code in Z80 cog could use the streamer for video.
This pic doesn't look quite right, at top of right palm tree trunk.
Not sure what you're talking about. The graphics in this scene are a bit janky as a still frame due to the heat effect.
Will the 68K and Z80 emulators both contain PSRAM code? If so, a single PSRAM cog would appear to be better so that spare code in Z80 cog could use the streamer for video.
Ye, the PSRAM code will be in both. It needs to be for lowest latency.
After looking at these CPU emulators you've been developing @Wuerfel_21 I now wonder how hard an AVR would be to emulate on a P2? It might be good for larger programs running from PSRAM. Especially given full GCC and C++ toolchain support for this microarchitecture. It wouldn't be as fast (maybe just a few MIPs instead of 16MIPs) but it could be useful for external memory program expansion and it might be a reasonable match with the performance of a PSRAM random read anyway.
After a quick look it seems like it should fit in a COG okay. I've started looking at the decoding and the flag stuff it might need. Idea is a LUT table holding EXECF vectors taking up 256 entries and indexed with RDLUT by upper byte of opcode. Regs stored in COGRAM and they could be indirectly indexed by setbyte/getbyte perhaps to maintain their 8 bit nature. ALU flags update will slow things a bit but many of the instructions would be simple. Nibble aligned register addresses helps a lot.
AVR is probably possible, but I don't see the point. It's not going to be fast enough to emulate existing code and why would you limit yourself to an 8 bit ISA otherwise...
I am however thinking that it is probably possible to squeeze an entire SNES audio board into a single cog. That's an SPC700 CPU (=6502 clone) at 1MHz, 64k of RAM and a moderately complex custom DSP that mixes 8 BRR-compressed samples with envelopes at 32kHz. The whole thing is effectively standalone, so you only need a 64k memory dump to play music (as opposed to a large register log).
In actual news, Z80 core is good enough to run some tests now:
It would be slow yes, but it may possibly allow some simple Arduino or other AVR code to run...lack of I/O peripherals would be an issue of course.
I've hacked up the bulk of it and it will certainly fit in a COG. The various flags are a problem that can slow the ALU ops down. Other ops are not so bad. If we could get a couple of MIPs from it then it might still be useful for something.
Ideally we could run 32 bit P2 operations not 8 bit AVR operations from external memory but we don't have the tools needed yet.
Wonder how the speed compares when running GCC-compiled code via 68000 emulation vs AVR emulation.... 68000 ops are slow to decode, but can handle 32 bits in one go...
Megayume's 68000 kore seems to be quite a bit faster than an 8MHz 68000 and it could be a bit faster if you removed things like interrupt/trace support and simplified the memory decoding.
(Also, I just remembered I could/should move some more addressing modes into cog memory with EXECF, which would see a neat bit of speedup)
Yeah it would be interesting and probably somewhat application dependent. The AVR may get a relative speedup with memory transfers and branches that normally take extra cycles but ALU would be slower with the flags. I've got the basic MOV instructions down to 29 clocks (cheating a bit with HUB RAM + fifo use for now). So a 300 MHz P2 could do about 10 AVR MIPs in MOV instructions, not too bad as a LOT of code is MOV (as well as load and store). It would be neat to tweak the AVR instructions to use 32 bits but no toolchain would like it.
Hmm, not counting opcode fetch overhead, a MOVE.L Dn,Dn takes... 130 cycles? Probably some miscounting in there. So on the incredibly silly front of register bandwidth, your AVR thing wins ;3
mk_nextop
mk_ihook1 nop
mk_ihook2 nop
call mk_getopf ' count as 8 cy for comparsions sake
push #mk_nextop
getnib mk_memtmp0,mk_opword,#3
altd mk_memtmp0,#mk_nibble_impl_tbl
jmp 0-0
mk_nibble_2 ' MOVE (long)
callpb mk_opword,#mk_setup_operand32
mk_setup_operand32
mov mk_shiftit,#0
test pb,#%110_000 wz
if_z jmp #mk_setup_reg32
mk_setup_reg32
and pb,#%1_111
sets mk_rd32_reg,pb
setd mk_wr32_reg,pb
mov mk_readf,#mk_rd32_reg
mov mk_writef,#mk_wr32_reg
ret wcz
call mk_readf
mk_rd32_reg
_ret_ mov mk_memvalue,0-0
callpa #31,#mk_move_shoot_the_Smile
mk_move_shoot_the_Smile ' handle all the common MOVE stuff
' Doing MOVEA?
test mk_opword,#%110_000_000 wz
testb mk_opword,#6 andz
if_z jmp #.movea
signx mk_memvalue,pa wcz
bitc mk_sr,#MK_NEG_BIT
bitz mk_sr,#MK_ZERO_BIT
andn mk_sr,#MK_OVER_MASK|MK_CARRY_MASK
.mangle_ea2 ' format for second operand is stupid
setnib mk_opword,#0,#3
mov pa,mk_opword
and pa,#%111_000_000
shl pa,#6
or mk_opword,pa
_ret_ shr mk_opword,#9
callpb mk_opword,#mk_setup_operand32
mk_setup_operand32
mov mk_shiftit,#0
test pb,#%110_000 wz
if_z jmp #mk_setup_reg32
mk_setup_reg32
and pb,#%1_111
sets mk_rd32_reg,pb
setd mk_wr32_reg,pb
mov mk_readf,#mk_rd32_reg
mov mk_writef,#mk_wr32_reg
ret wcz
call mk_readf
mk_rd32_reg
_ret_ mov mk_memvalue,0-0
jmp mk_writef
mk_wr32_reg
_ret_ mov 0-0,mk_memvalue
I guess MOVE and a bunch of other ops don't really care about mk_shiftit that much, so that's 4 cycles that could be eliminated by jumping over that.
@rogloh said:
Yeah it would be interesting and probably somewhat application dependent. The AVR may get a relative speedup with memory transfers and branches that normally take extra cycles but ALU would be slower with the flags. I've got the basic MOV instructions down to 29 clocks (cheating a bit with HUB RAM + fifo use for now). So a 300 MHz P2 could do about 10 AVR MIPs in MOV instructions, not too bad as a LOT of code is MOV (as well as load and store). It would be neat to tweak the AVR instructions to use 32 bits but no toolchain would like it.
Will this work? Low byte of instr gets overwritten in line 2.
How about using XBYTE? The end of each instruction could read the low byte of the next opcode:
_ret_ rfbyte oplow
where TOS = $1FF and _ ret _ starts new XBYTE using high byte of opcode, copying it to pa. Most AVR instructions can be decoded using the high seven bits, halving LUT EXECF table to 128 longs. This means extra decoding for some instructions but adds only two cycles to MOVW:
@TonyB_ said:
Will this work? Low byte of instr gets overwritten in line 2.
Yeah I found that today and fixed it.
How about using XBYTE? The end of each instruction could read the low byte of the next opcode:
_ret_ rfbyte oplow
Haven't looked at that yet. Might try it once I've put all the other things together and got something going there. It will fit fine in the COG with a 256 entry table and this allows high/low register selection in the execf sequence (see regbase vs regbase+4 alternatives below).
The AVR ISA is reasonably simple to emulate but as expected the flags are a PITA and chew more P2 cycles. Here's a sample of what I've got (untested and I'm not even sure I have its logic coded right). AVR uses a half carry flag, and an overflow flag too in ALU operations which are annoying to compute, as well as the more typical C, Z, S, N flags which are okay. I think the ADD here alone takes about 50 P2 clocks plus the outer loop overhead time of about 14 P2 clocks (total 64 clocks, so a bit under 5MIPs @ 300MHz...but could still be usable). Thankfully most other instructions are much simpler/faster than these.
op_cpc
op_cp
op_sbc
op_sub
op_add
op_adc
op_cpi
op_sbci
op_subi
getnib d, instr, #1 ' CPC CP SBC SUB ADD ADC CPI SBCI SUBI
altgb d, #regbase ' l l l l l l l l l
altgb d, #regbase+4 ' h h h h h l l l l
getbyte d1, 0-0, #0 ' CPC CP SBC SUB ADD ADC CPI SBCI SUBI
getnib s, instr, #0 ' CPC CP SBC SUB ADD ADC | | |
altgb s, #regbase ' l l l l l l | | |
altgb s, #regbase+4 ' h h h h h h | | |
getbyte s1, 0-0, #0 ' CPC CP SBC SUB ADD ADC | | |
getnib s1, instr, #2 ' | | | | | | CPI SBCI SUBI
rolnib s1, instr, #0 ' | | | | | | CPI SBCI SUBI
getnib d2, d1, #0 ' CPC CP SBC SUB ADD ADC CPI SBCI SUBI ' save for flags
testb flags, #CFLAG wc ' CPC | SBC | | ADC | SBCI |
subx d1, s1 wz ' | | SBC | | | | SBCI |
add d1, s1 ' | | | | ADD | | | |
sub d1, s1 wz ' | | | SUB | | | | SUBI
addx d1, s1 ' | | | | | ADC | | |
cmp d1, s1 wz ' | CP | | | | CPI | |
cmpx d1, s1 wz ' CPC | | | | | CPI | |
altsb d, #regbase ' | | l l l l | l l
altsb d, #regbase+4 ' | | h h h l | l l
setbyte 0-0, d1, #0 ' | | SBC SUB ADD ADC | SBCI SUBI
mov d, d1 ' CPC CP SBC SUB ADD ADC CPI SBCI SUBI
fles d, #127 wc ' CPC CP SBC SUB ADD ADC CPI SBCI SUBI
if_nc fges d, minus128 wc ' CPC CP SBC SUB ADD ADC CPI SBCI SUBI
bitc flags, #VFLAG ' CPC CP SBC SUB ADD ADC CPI SBCI SUBI
test d1, #255 wz ' | ADD ADC
testb d1, #8 wc ' | ADD ADC
bitc flags, #CFLAG ' | ADD ADC
testb flags, #ZFLAG andz ' CPC SBC SBCI
bitz flags, #ZFLAG ' CPC CP SBC SUB ADD ADC CPI SBCI SUBI
testb d1, #7 wc ' CPC CP SBC SUB ADD ADC CPI SBCI SUBI
bitc flags, #NFLAG ' CPC CP SBC SUB ADD ADC CPI SBCI SUBI
testb flags, #VFLAG xorc ' CPC CP SBC SUB ADD ADC CPI SBCI SUBI
bitc flags, #SFLAG ' CPC CP SBC SUB ADD ADC CPI SBCI SUBI
and s1, #$f ' CPC CP SBC SUB ADD ADC CPI SBCI SUBI
cmp d2, s1 wc ' CP SUB | | CPI SUBI
cmpx d2, s1 wc ' CPC SBC | | SBCI
add d2, s1 wc ' ADD |
addx d2, s1 wc ' | ADC
_ret_ bitc flags, #HFLAG ' CPC CP SBC SUB ADD ADC CPI SBCI SUBI
mov temp,dest
add dest,src 'arithmetic operation
xor temp,src
xor temp,dest 'temp = dest ^ src ^ result
'temp[bit] = carry into result[bit]
'overflow if carry into result[msb] != carry out of result[msb]
testb dest,#8 wc
bitc flags,#CF
testb temp,#7 xorc
bitc flags,#VF
testb temp,#4
bitc flags,#HF
I notice that rather stupidly neither of the AVR sign and half-carry bits in SREG match the corresponding bits in the result (7 & 4), unlike flag reg in 8080/Z80.
Yeah, flags are a PITA. I use the same idea as Tony to compute C/H/V flags.
What about SuperH?
That ISA is 32 bit and only has one status bit (called T) that isn't even written by the basic ADD/SUB and all the opcode fields are pleasantly nibble aligned, unlike 68000. Though obnoxiously, it's the top and bottom nibbles of the 16 bit instruction that determine the operation and the middle two nibbles select the registers.
Or maybe try getting Eric's RISC-V recompiler to deal with external memory...
@rogloh said:
After looking at these CPU emulators you've been developing @Wuerfel_21 I now wonder how hard an AVR would be to emulate on a P2? It might be good for larger programs running from PSRAM. Especially given full GCC and C++ toolchain support for this microarchitecture. It wouldn't be as fast (maybe just a few MIPs instead of 16MIPs) but it could be useful for external memory program expansion and it might be a reasonable match with the performance of a PSRAM random read anyway.
After a quick look it seems like it should fit in a COG okay. I've started looking at the decoding and the flag stuff it might need. Idea is a LUT table holding EXECF vectors taking up 256 entries and indexed with RDLUT by upper byte of opcode. Regs stored in COGRAM and they could be indirectly indexed by setbyte/getbyte perhaps to maintain their 8 bit nature. ALU flags update will slow things a bit but many of the instructions would be simple. Nibble aligned register addresses helps a lot.
A better target may be the Zylin ZPU. It has a GCC target, and there's already a P1 implementation of it. It's made to be very small to implement in an FPGA, and not particularly fast.
Okay, Z80 seems to work "good enough" now. All the documented features are there and most of the undocumented ones, too. No interrupts yet. Computed cycle counts are off in some cases, but in the right ballpark, I think.
Now I'll need to fit it and the OPN into the emulator proper. That shouldn't be too much work, though the OPN needs a PASM I/O interface and timers implemented.
@Wuerfel_21 said:
Now I'll need to fit it and the OPN into the emulator proper. That shouldn't be too much work, though the OPN needs a PASM I/O interface and timers implemented.
Cool, will check this out, could save me some cycles, as well as the XBYTE thing. Maybe this AVR could run at a reasonable speed in the end (at least from HUB).
I've got this weird idea to try to somehow use FBLOCK and PSRAM reads into a cycling HUB region for the FIFO to use, tracking the emulated PC as we go and using the FIFO wrap interrupt too. Needs more thought but something like it may work ok for emulating from external RAM....
Cool, will check this out, could save me some cycles, as well as the XBYTE thing. Maybe this AVR could run at a reasonable speed in the end (at least from HUB).
The double XOR trick should save a few cycles. Main advantage is no need to do extra 4-bit arithmetic operation to get half-carry. The best I can do Z80 ADD A/ADC A/SUB/SBC A flags is 22 cycles, which includes YF & XF for free. CP s takes 26 cycles as YF & XF come from s, not the result.
One thing is very clear. If a future P2+/P3 had a new FLAGS D instruction (perhaps involving SETQ) to handle legacy CPU flags (Z80 and 8086 at least) then the time savings would be huge. A new MOVBITS D,S that moves bits within low byte of D as given by S could convert supported flags to other CPUs and generally would be very handy.
MOVBYTS D,{#}S could change to MOVBYTS D,#S and MOVBITS D,S.
I've got this weird idea to try to somehow use FBLOCK and PSRAM reads into a cycling HUB region for the FIFO to use, tracking the emulated PC as we go and using the FIFO wrap interrupt too. Needs more thought but something like it may work ok for emulating from external RAM....
It would be great if you could get PSRAM and XBYTE working together. Automatic FIFO wrapping using RDFAST seems to be impossible for CPU emulators because the wrap address needs to be a fixed number of blocks from a base address (CPU address zero), not the start address (CPU PC). Perhaps FBLOCK could solve this?
@TonyB_ 22-26 cycles for flags seems about right. I've got my ALU stuff for AVR down to this below (still untested, could have bugs)...
By the way if @Wuerfel_21 doesn't want these additional CPU emulator discussions cluttering up her console emulation thread, happy to start a new thread, although there are two CPU emulators, 68k and Z80 currently being worked on here, so dunno where it fits.
It would be great if you could PSRAM and XBYTE working together. Automatic FIFO wrapping using RDFAST seems to be impossible for CPU emulators because the wrap address needs to be a fixed number of blocks from a base address (CPU address zero), not the start address (CPU PC). Perhaps FBLOCK could solve this?
Hoping it might somehow, and if I can dynamically read into smaller 64 byte blocks and effectively create some type of I-cache... I wonder if that FIFO interrupt can be triggered at the end of reading the last byte/word/long from a block before we are about to wrap back to the beginning or it if happens AFTER you just wrapped, and have already read the first byte from the beginning of the block. If it's the former, we may have a way to read in another block on the fly when we need to before using an out of date instruction (TBD). Perhaps the block address could be re-allocated to one using another area of HUB RAM already read (forming some type of rudimentary I-cache). Those are my nebulous thoughts so far anyway.
op_cpc
op_cp
op_sbc
op_sub
op_add
op_adc
op_cpi
op_sbci
op_subi
getnib d, instr, #1 ' CPC CP SBC SUB ADD ADC CPI SBCI SUBI
altgb d, #regbase ' l l l l l l l l l
altgb d, #regbase+4 ' h h h h h l l l l
getbyte d1, 0-0, #0 ' CPC CP SBC SUB ADD ADC CPI SBCI SUBI
getnib s, instr, #0 ' CPC CP SBC SUB ADD ADC | | |
altgb s, #regbase ' l l l l l l | | |
altgb s, #regbase+4 ' h h h h h h | | |
getbyte s1, 0-0, #0 ' CPC CP SBC SUB ADD ADC | | |
getnib s1, instr, #2 ' | | | | | | CPI SBCI SUBI
rolnib s1, instr, #0 ' | | | | | | CPI SBCI SUBI
getbyte d2, d1, #0 ' CPC CP SBC SUB ADD ADC CPI SBCI SUBI
testb flags, #CFLAG wc ' CPC | SBC | | ADC | SBCI |
subx d1, s1 wz ' CPC | SBC | | | | SBCI |
add d1, s1 ' | | | | ADD | | | |
sub d1, s1 wz ' | CP | SUB | | CPI | SUBI
addx d1, s1 ' | | | | | ADC | | |
altsb d, #regbase ' | | l l l l | l l
altsb d, #regbase+4 ' | | h h h l | l l
setbyte 0-0, d1, #0 ' | | SBC SUB ADD ADC | SBCI SUBI
test d1, #$ff wz ' | | | | ADD ADC | | |
testb flags, #ZFLAG andz ' CPC | SBC | | | | SBCI |
bitz flags, #ZFLAG ' CPC CP SBC SUB ADD ADC CPI SBCI SUBI
xor d2, s1 ' CPC CP SBC SUB ADD ADC CPI SBCI SUBI
xor d2, d1 ' CPC CP SBC SUB ADD ADC CPI SBCI SUBI
testb d1, #7 wc ' CPC CP SBC SUB ADD ADC CPI SBCI SUBI
bitc flags, #NFLAG ' CPC CP SBC SUB ADD ADC CPI SBCI SUBI
testb d1, #8 wc ' CPC CP SBC SUB ADD ADC CPI SBCI SUBI
bitc flags, #CFLAG ' CPC CP SBC SUB ADD ADC CPI SBCI SUBI
testb d2, #7 xorc ' CPC CP SBC SUB ADD ADC CPI SBCI SUBI
bitc flags, #VFLAG ' CPC CP SBC SUB ADD ADC CPI SBCI SUBI
testb flags, #NFLAG xorc ' CPC CP SBC SUB ADD ADC CPI SBCI SUBI
bitc flags, #SFLAG ' CPC CP SBC SUB ADD ADC CPI SBCI SUBI
testb d2, #4 wc ' CPC CP SBC SUB ADD ADC CPI SBCI SUBI
_ret_ bitc flags, #HFLAG ' CPC CP SBC SUB ADD ADC CPI SBCI SUBI
@rogloh said:
Hoping it might somehow, and if I can dynamically read into smaller 64 byte blocks and effectively create some type of I-cache... I wonder if that FIFO interrupt can be triggered at the end of reading the last byte/word/long from a block before we are about to wrap back to the beginning or it if happens AFTER you just wrapped, and have already read the first byte from the beginning of the block. If it's the former, we may have a way to read in another block on the fly when we need to before using an out of date instruction (TBD). Perhaps the block address could be re-allocated to one using another area of HUB RAM already read (forming some type of rudimentary I-cache). Those are my nebulous thoughts so far anyway.
Reading the docs ... The FBW event occurs after the contiguous blocks are completed and it has started the next lot. FBLOCK commands are buffered just like the streamer commands.
Therefore to make effective use of FBLOCK for a random block list, you have to load up two block commands before the first FBW event gets triggered. So start with the RDFAST for the first block (with block count of one). Then immediately issue FBLOCK for the second block (also with block count of one). Then enable interrupts, or in the main loop, upon FBW event, issue another FBLOCK (each one having a block count of one).
At time of FBW event, for counts of one, the issued FBLOCK is for a whole block in the future of where the emulator is decoding.
PS: Also, when using non-zero block counts, all start addresses have to be longword aligned.
Although the wrap address could (and should) be on a 64-byte boundary, the RDFAST start address could be anywhere within a 64-byte block. This might be a problem as the block count starts from the RDFAST address.
If required, could the PSRAM code start the streamer before the PSRAM is ready and stream in rubbish data before the desired start address data? This would have to be done only for the RDFAST block.
@TonyB_ said:
Although the wrap address could (and should) be on a 64-byte boundary, ...
Only has to be longword aligned. But each block is 64 bytes in size. So, if not all 64 bytes is wanted you still have to read the remainder out of the FIFO before the new block appears.
The alternative is to start again with a fresh RDFAST ... Which maybe a suitable solution because by using a $8000_0000 for the block count it'll fetch in the background and if you've got other things to attend while the FIFO fills then bobs-your-uncle.
And what's more, $8000_0000 is treated as a zero block count. Which means byte alignment is okay to use.
@evanh said:
PS: Also, when using non-zero block counts, all start addresses have to be longword aligned.
Is this another problem, that rules out automatic wrapping with RDFAST & FBLOCK? On branching, first byte in FIFO must be opcode at exact jump or call address, not up to 3 bytes lower.
@evanh said:
PS: Also, when using non-zero block counts, all start addresses have to be longword aligned.
Is this another problem, that rules out automatic wrapping with RDFAST & FBLOCK? On branching, first byte in FIFO must be opcode at exact jump or call address, not up to 3 bytes lower.
I figured, with fixed 64-byte blocks, wasted fetches all round was going to be order of things.
PS: Note, as above, zero count can be byte aligned.
Comments
This pic doesn't look quite right, at top of right palm tree trunk.
Will the 68K and Z80 emulators both contain PSRAM code? If so, a single PSRAM cog would appear to be better so that spare code in Z80 cog could use the streamer for video.
Not sure what you're talking about. The graphics in this scene are a bit janky as a still frame due to the heat effect.
Ye, the PSRAM code will be in both. It needs to be for lowest latency.
Looks corrupted to right of "SONIC GOT" and "THROUGH".
That's just the "ACT 1" icon.
So, uhh, making some inroads on that Z80 kore.
Why are the block operations so insane?
Why did I decide to write it like that?
AAAAAAAAA
.blockop '' The undocumented flags on these are cursed. test zk_opcode,#%0100_1000 wz if_nz ret ' NOP rczr zk_opcode wcz ' get operation type into cz if_00 skipf ##%00000000_11101_01_1111110_0110_011_111111 if_01 skipf ##%00000011_00000_10_0011110_0101_011_1111 if_10 skipf ##%00001111_11101_01_1100011_0011_100_11 if_11 skipf ##%00111111_11101_01_1111101_0011_011 getbyte zk_ea,zk_debc,#0 ' IN call #\zk_portin ' IN call #\zk_read8hl ' everything else modc _clr wc ' LD modc _set wc ' CP testb zk_tmp8,#7 wc ' IN/OUT bitc zk_flags,#ZK_NMODE_BIT mov zk_optmp0,zk_accu ' LD CP getbyte zk_optmp0,zk_hl,#0 ' OUT getbyte zk_optmp0,zk_debc,#0 ' IN testb zk_opcode,#1 wc ' IN sumc zk_optmp0,#1 ' IN mov zk_optmp1,zk_tmp8 ' CP xor zk_optmp1,zk_accu ' CP sub zk_optmp0,zk_tmp8 ' CP only add zk_optmp0,zk_tmp8 ' LD,IN,OUT xor zk_optmp1,zk_optmp0 ' CP only and zk_optmp0,#255 wz bitz zk_flags,#ZK_ZERO_BIT ' CP testb zk_optmp0,#7 wc ' CP bitc zk_optmp0,#ZK_SIGN_BIT ' CP skipf ##%000_00_000_0_1110100_1100_1111_0000_11111_111111 skipf ##%000_00_111_0_1110100_1111_1111_0000_01010_1111 skipf ##%000_00_111_0_0001001_1111_0000_1111_10101_11 skipf ##%000_00_111_0_0001001_0011_0000_1111_10101 testb zk_optmp1,#4 wc ' CP cmpr zk_optmp0,#255 wc ' IN/OUT bitc zk_flags,#ZK_HALF_BIT ' CP muxc zk_flags,#(1<<ZK_HALF_BIT)|(1<<ZK_CARRY_BIT) ' IN/OUT if_c sub zk_optmp0,#1 ' CP testb zk_optmp0,#1 wc ' LD,CP bitc zk_flags,#3 'LD,CP (sets YF) testb zk_optmp0,#3 wc ' LD,CP bitc zk_flags,#5 'LD,CP (sets XF) getbyte zk_optmp1,zk_debc,#1 ' IN,OUT (get B) and zk_optmp0,#7 ' IN,OUT xor zk_optmp0,zk_optmp1 wc ' IN,OUT bitnc zk_flags,#ZK_OVER_BIT ' IN,OUT getword zk_ea,zk_debc,#1 ' LD call #\zk_write8 ' LD getbyte zk_ea,zk_debc,#0 ' OUT call #\zk_portout ' OUT getword zk_optmp1,zk_debc,#0 ' LD,CP decmod zk_optmp1,zk_ffffh wz ' all setbyte zk_debc,zk_ea,#1 ' IN/OUT bitnz zk_flags,#ZK_OVER_BIT ' LD,CP bitz zk_flags,#ZK_ZERO_BIT ' IN,OUT setq #ZK_SIGNXYMASK ' IN,OUT muxq zk_flags,zk_optmp1 ' IN,OUT testb zk_opcode,#1 wc ' Get direction (C = dec) if_nc incmod zk_ea,zk_ffffh ' LD if_c decmod zk_ea,zk_ffffh ' LD setword zk_debc,zk_ea,#1 ' LD if_nc incmod zk_hl,zk_ffffh if_c decmod zk_hl,zk_ffffh testb zk_opcode,#2 wc ' Is repeat code? if_c_and_nz sub zk_pc,#2 retThe best part is that there's surely a bug in there. IDK, still too lazy to set up an assembler to run some code yet.
LOL. Nested skipfs are so much fun to maintain. Just wait when you need to fit another line in.
Just wait when you need to fit another line in.
After looking at these CPU emulators you've been developing @Wuerfel_21 I now wonder how hard an AVR would be to emulate on a P2? It might be good for larger programs running from PSRAM. Especially given full GCC and C++ toolchain support for this microarchitecture. It wouldn't be as fast (maybe just a few MIPs instead of 16MIPs) but it could be useful for external memory program expansion and it might be a reasonable match with the performance of a PSRAM random read anyway.
Here's the ISA:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Atmel_AVR_instruction_set
After a quick look it seems like it should fit in a COG okay. I've started looking at the decoding and the flag stuff it might need. Idea is a LUT table holding EXECF vectors taking up 256 entries and indexed with RDLUT by upper byte of opcode. Regs stored in COGRAM and they could be indirectly indexed by setbyte/getbyte perhaps to maintain their 8 bit nature. ALU flags update will slow things a bit but many of the instructions would be simple. Nibble aligned register addresses helps a lot.
AVR is probably possible, but I don't see the point. It's not going to be fast enough to emulate existing code and why would you limit yourself to an 8 bit ISA otherwise...
I am however thinking that it is probably possible to squeeze an entire SNES audio board into a single cog. That's an SPC700 CPU (=6502 clone) at 1MHz, 64k of RAM and a moderately complex custom DSP that mixes 8 BRR-compressed samples with envelopes at 32kHz. The whole thing is effectively standalone, so you only need a 64k memory dump to play music (as opposed to a large register log).
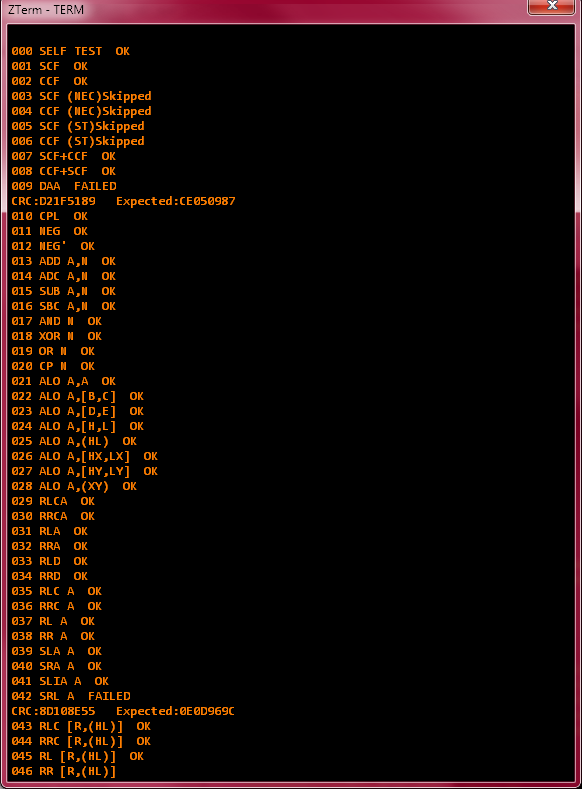
In actual news, Z80 core is good enough to run some tests now:
It would be slow yes, but it may possibly allow some simple Arduino or other AVR code to run...lack of I/O peripherals would be an issue of course.
I've hacked up the bulk of it and it will certainly fit in a COG. The various flags are a problem that can slow the ALU ops down. Other ops are not so bad. If we could get a couple of MIPs from it then it might still be useful for something.
Ideally we could run 32 bit P2 operations not 8 bit AVR operations from external memory but we don't have the tools needed yet.
Wonder how the speed compares when running GCC-compiled code via 68000 emulation vs AVR emulation.... 68000 ops are slow to decode, but can handle 32 bits in one go...
Megayume's 68000 kore seems to be quite a bit faster than an 8MHz 68000 and it could be a bit faster if you removed things like interrupt/trace support and simplified the memory decoding.
(Also, I just remembered I could/should move some more addressing modes into cog memory with EXECF, which would see a neat bit of speedup)
Yeah it would be interesting and probably somewhat application dependent. The AVR may get a relative speedup with memory transfers and branches that normally take extra cycles but ALU would be slower with the flags. I've got the basic MOV instructions down to 29 clocks (cheating a bit with HUB RAM + fifo use for now). So a 300 MHz P2 could do about 10 AVR MIPs in MOV instructions, not too bad as a LOT of code is MOV (as well as load and store). It would be neat to tweak the AVR instructions to use 32 bits but no toolchain would like it.
loop rfword instr ' 2 ' need to wrap? getbyte instr, instr, #1 ' 2 rdlut sequence, instr '3 push #loop ' 2 execf sequence ' 4 getnib s, instr, #0 ' 2 getnib d, instr, #1 ' 2 altgb s, #regbase ' 2 getbyte s, 0-0, #0 ' 2 mov d1, s ' 2 (done like this to share code) altsb d, #regbase ' 2 _ret_ setbyte 0-0, d1, #0 ' 4Hmm, not counting opcode fetch overhead, a MOVE.L Dn,Dn takes... 130 cycles? Probably some miscounting in there. So on the incredibly silly front of register bandwidth, your AVR thing wins ;3
mk_nextop mk_ihook1 nop mk_ihook2 nop call mk_getopf ' count as 8 cy for comparsions sake push #mk_nextop getnib mk_memtmp0,mk_opword,#3 altd mk_memtmp0,#mk_nibble_impl_tbl jmp 0-0 mk_nibble_2 ' MOVE (long) callpb mk_opword,#mk_setup_operand32 mk_setup_operand32 mov mk_shiftit,#0 test pb,#%110_000 wz if_z jmp #mk_setup_reg32 mk_setup_reg32 and pb,#%1_111 sets mk_rd32_reg,pb setd mk_wr32_reg,pb mov mk_readf,#mk_rd32_reg mov mk_writef,#mk_wr32_reg ret wcz call mk_readf mk_rd32_reg _ret_ mov mk_memvalue,0-0 callpa #31,#mk_move_shoot_the_Smile mk_move_shoot_the_Smile ' handle all the common MOVE stuff ' Doing MOVEA? test mk_opword,#%110_000_000 wz testb mk_opword,#6 andz if_z jmp #.movea signx mk_memvalue,pa wcz bitc mk_sr,#MK_NEG_BIT bitz mk_sr,#MK_ZERO_BIT andn mk_sr,#MK_OVER_MASK|MK_CARRY_MASK .mangle_ea2 ' format for second operand is stupid setnib mk_opword,#0,#3 mov pa,mk_opword and pa,#%111_000_000 shl pa,#6 or mk_opword,pa _ret_ shr mk_opword,#9 callpb mk_opword,#mk_setup_operand32 mk_setup_operand32 mov mk_shiftit,#0 test pb,#%110_000 wz if_z jmp #mk_setup_reg32 mk_setup_reg32 and pb,#%1_111 sets mk_rd32_reg,pb setd mk_wr32_reg,pb mov mk_readf,#mk_rd32_reg mov mk_writef,#mk_wr32_reg ret wcz call mk_readf mk_rd32_reg _ret_ mov mk_memvalue,0-0 jmp mk_writef mk_wr32_reg _ret_ mov 0-0,mk_memvalueI guess MOVE and a bunch of other ops don't really care about
mk_shiftitthat much, so that's 4 cycles that could be eliminated by jumping over that.Will this work? Low byte of instr gets overwritten in line 2.
How about using XBYTE? The end of each instruction could read the low byte of the next opcode:
where TOS = $1FF and _ ret _ starts new XBYTE using high byte of opcode, copying it to pa. Most AVR instructions can be decoded using the high seven bits, halving LUT EXECF table to 128 longs. This means extra decoding for some instructions but adds only two cycles to MOVW:
What test program are you using? Some mnemonics are not Z80.
You mean "ALO"? That's just a catch-all for all the opcodes $80..$BF
Yeah I found that today and fixed it.
Haven't looked at that yet. Might try it once I've put all the other things together and got something going there. It will fit fine in the COG with a 256 entry table and this allows high/low register selection in the execf sequence (see regbase vs regbase+4 alternatives below).
The AVR ISA is reasonably simple to emulate but as expected the flags are a PITA and chew more P2 cycles. Here's a sample of what I've got (untested and I'm not even sure I have its logic coded right). AVR uses a half carry flag, and an overflow flag too in ALU operations which are annoying to compute, as well as the more typical C, Z, S, N flags which are okay. I think the ADD here alone takes about 50 P2 clocks plus the outer loop overhead time of about 14 P2 clocks (total 64 clocks, so a bit under 5MIPs @ 300MHz...but could still be usable). Thankfully most other instructions are much simpler/faster than these.
op_cpc op_cp op_sbc op_sub op_add op_adc op_cpi op_sbci op_subi getnib d, instr, #1 ' CPC CP SBC SUB ADD ADC CPI SBCI SUBI altgb d, #regbase ' l l l l l l l l l altgb d, #regbase+4 ' h h h h h l l l l getbyte d1, 0-0, #0 ' CPC CP SBC SUB ADD ADC CPI SBCI SUBI getnib s, instr, #0 ' CPC CP SBC SUB ADD ADC | | | altgb s, #regbase ' l l l l l l | | | altgb s, #regbase+4 ' h h h h h h | | | getbyte s1, 0-0, #0 ' CPC CP SBC SUB ADD ADC | | | getnib s1, instr, #2 ' | | | | | | CPI SBCI SUBI rolnib s1, instr, #0 ' | | | | | | CPI SBCI SUBI getnib d2, d1, #0 ' CPC CP SBC SUB ADD ADC CPI SBCI SUBI ' save for flags testb flags, #CFLAG wc ' CPC | SBC | | ADC | SBCI | subx d1, s1 wz ' | | SBC | | | | SBCI | add d1, s1 ' | | | | ADD | | | | sub d1, s1 wz ' | | | SUB | | | | SUBI addx d1, s1 ' | | | | | ADC | | | cmp d1, s1 wz ' | CP | | | | CPI | | cmpx d1, s1 wz ' CPC | | | | | CPI | | altsb d, #regbase ' | | l l l l | l l altsb d, #regbase+4 ' | | h h h l | l l setbyte 0-0, d1, #0 ' | | SBC SUB ADD ADC | SBCI SUBI mov d, d1 ' CPC CP SBC SUB ADD ADC CPI SBCI SUBI fles d, #127 wc ' CPC CP SBC SUB ADD ADC CPI SBCI SUBI if_nc fges d, minus128 wc ' CPC CP SBC SUB ADD ADC CPI SBCI SUBI bitc flags, #VFLAG ' CPC CP SBC SUB ADD ADC CPI SBCI SUBI test d1, #255 wz ' | ADD ADC testb d1, #8 wc ' | ADD ADC bitc flags, #CFLAG ' | ADD ADC testb flags, #ZFLAG andz ' CPC SBC SBCI bitz flags, #ZFLAG ' CPC CP SBC SUB ADD ADC CPI SBCI SUBI testb d1, #7 wc ' CPC CP SBC SUB ADD ADC CPI SBCI SUBI bitc flags, #NFLAG ' CPC CP SBC SUB ADD ADC CPI SBCI SUBI testb flags, #VFLAG xorc ' CPC CP SBC SUB ADD ADC CPI SBCI SUBI bitc flags, #SFLAG ' CPC CP SBC SUB ADD ADC CPI SBCI SUBI and s1, #$f ' CPC CP SBC SUB ADD ADC CPI SBCI SUBI cmp d2, s1 wc ' CP SUB | | CPI SUBI cmpx d2, s1 wc ' CPC SBC | | SBCI add d2, s1 wc ' ADD | addx d2, s1 wc ' | ADC _ret_ bitc flags, #HFLAG ' CPC CP SBC SUB ADD ADC CPI SBCI SUBIThis is how I do H and V flags:
mov temp,dest add dest,src 'arithmetic operation xor temp,src xor temp,dest 'temp = dest ^ src ^ result 'temp[bit] = carry into result[bit] 'overflow if carry into result[msb] != carry out of result[msb] testb dest,#8 wc bitc flags,#CF testb temp,#7 xorc bitc flags,#VF testb temp,#4 bitc flags,#HFI notice that rather stupidly neither of the AVR sign and half-carry bits in SREG match the corresponding bits in the result (7 & 4), unlike flag reg in 8080/Z80.
Yeah, flags are a PITA. I use the same idea as Tony to compute C/H/V flags.
What about SuperH?
That ISA is 32 bit and only has one status bit (called T) that isn't even written by the basic ADD/SUB and all the opcode fields are pleasantly nibble aligned, unlike 68000. Though obnoxiously, it's the top and bottom nibbles of the 16 bit instruction that determine the operation and the middle two nibbles select the registers.
Or maybe try getting Eric's RISC-V recompiler to deal with external memory...
It is on... Me vs. the last damn instruction.
And of course it's one that's implemented by that mess I've shown earlier (which I've already fixed plenty of bugs in)
A better target may be the Zylin ZPU. It has a GCC target, and there's already a P1 implementation of it. It's made to be very small to implement in an FPGA, and not particularly fast.
Okay, Z80 seems to work "good enough" now. All the documented features are there and most of the undocumented ones, too. No interrupts yet. Computed cycle counts are off in some cases, but in the right ballpark, I think.
I've attached it and the compiled test program (source here (note that the newest version of sjasm is busted, use the previous one)), perhaps someone wants to compare it to @Cluso99 's Z80 core.
Now I'll need to fit it and the OPN into the emulator proper. That shouldn't be too much work, though the OPN needs a PASM I/O interface and timers implemented.
That's the fun part!
Cool, will check this out, could save me some cycles, as well as the XBYTE thing. Maybe this AVR could run at a reasonable speed in the end (at least from HUB).
I've got this weird idea to try to somehow use FBLOCK and PSRAM reads into a cycling HUB region for the FIFO to use, tracking the emulated PC as we go and using the FIFO wrap interrupt too. Needs more thought but something like it may work ok for emulating from external RAM....
The double XOR trick should save a few cycles. Main advantage is no need to do extra 4-bit arithmetic operation to get half-carry. The best I can do Z80 ADD A/ADC A/SUB/SBC A flags is 22 cycles, which includes YF & XF for free. CP s takes 26 cycles as YF & XF come from s, not the result.
One thing is very clear. If a future P2+/P3 had a new FLAGS D instruction (perhaps involving SETQ) to handle legacy CPU flags (Z80 and 8086 at least) then the time savings would be huge. A new MOVBITS D,S that moves bits within low byte of D as given by S could convert supported flags to other CPUs and generally would be very handy.
MOVBYTS D,{#}S could change to MOVBYTS D,#S and MOVBITS D,S.
It would be great if you could get PSRAM and XBYTE working together. Automatic FIFO wrapping using RDFAST seems to be impossible for CPU emulators because the wrap address needs to be a fixed number of blocks from a base address (CPU address zero), not the start address (CPU PC). Perhaps FBLOCK could solve this?
@TonyB_ 22-26 cycles for flags seems about right. I've got my ALU stuff for AVR down to this below (still untested, could have bugs)...
By the way if @Wuerfel_21 doesn't want these additional CPU emulator discussions cluttering up her console emulation thread, happy to start a new thread, although there are two CPU emulators, 68k and Z80 currently being worked on here, so dunno where it fits.
Hoping it might somehow, and if I can dynamically read into smaller 64 byte blocks and effectively create some type of I-cache... I wonder if that FIFO interrupt can be triggered at the end of reading the last byte/word/long from a block before we are about to wrap back to the beginning or it if happens AFTER you just wrapped, and have already read the first byte from the beginning of the block. If it's the former, we may have a way to read in another block on the fly when we need to before using an out of date instruction (TBD). Perhaps the block address could be re-allocated to one using another area of HUB RAM already read (forming some type of rudimentary I-cache). Those are my nebulous thoughts so far anyway.
op_cpc op_cp op_sbc op_sub op_add op_adc op_cpi op_sbci op_subi getnib d, instr, #1 ' CPC CP SBC SUB ADD ADC CPI SBCI SUBI altgb d, #regbase ' l l l l l l l l l altgb d, #regbase+4 ' h h h h h l l l l getbyte d1, 0-0, #0 ' CPC CP SBC SUB ADD ADC CPI SBCI SUBI getnib s, instr, #0 ' CPC CP SBC SUB ADD ADC | | | altgb s, #regbase ' l l l l l l | | | altgb s, #regbase+4 ' h h h h h h | | | getbyte s1, 0-0, #0 ' CPC CP SBC SUB ADD ADC | | | getnib s1, instr, #2 ' | | | | | | CPI SBCI SUBI rolnib s1, instr, #0 ' | | | | | | CPI SBCI SUBI getbyte d2, d1, #0 ' CPC CP SBC SUB ADD ADC CPI SBCI SUBI testb flags, #CFLAG wc ' CPC | SBC | | ADC | SBCI | subx d1, s1 wz ' CPC | SBC | | | | SBCI | add d1, s1 ' | | | | ADD | | | | sub d1, s1 wz ' | CP | SUB | | CPI | SUBI addx d1, s1 ' | | | | | ADC | | | altsb d, #regbase ' | | l l l l | l l altsb d, #regbase+4 ' | | h h h l | l l setbyte 0-0, d1, #0 ' | | SBC SUB ADD ADC | SBCI SUBI test d1, #$ff wz ' | | | | ADD ADC | | | testb flags, #ZFLAG andz ' CPC | SBC | | | | SBCI | bitz flags, #ZFLAG ' CPC CP SBC SUB ADD ADC CPI SBCI SUBI xor d2, s1 ' CPC CP SBC SUB ADD ADC CPI SBCI SUBI xor d2, d1 ' CPC CP SBC SUB ADD ADC CPI SBCI SUBI testb d1, #7 wc ' CPC CP SBC SUB ADD ADC CPI SBCI SUBI bitc flags, #NFLAG ' CPC CP SBC SUB ADD ADC CPI SBCI SUBI testb d1, #8 wc ' CPC CP SBC SUB ADD ADC CPI SBCI SUBI bitc flags, #CFLAG ' CPC CP SBC SUB ADD ADC CPI SBCI SUBI testb d2, #7 xorc ' CPC CP SBC SUB ADD ADC CPI SBCI SUBI bitc flags, #VFLAG ' CPC CP SBC SUB ADD ADC CPI SBCI SUBI testb flags, #NFLAG xorc ' CPC CP SBC SUB ADD ADC CPI SBCI SUBI bitc flags, #SFLAG ' CPC CP SBC SUB ADD ADC CPI SBCI SUBI testb d2, #4 wc ' CPC CP SBC SUB ADD ADC CPI SBCI SUBI _ret_ bitc flags, #HFLAG ' CPC CP SBC SUB ADD ADC CPI SBCI SUBIReading the docs ... The FBW event occurs after the contiguous blocks are completed and it has started the next lot. FBLOCK commands are buffered just like the streamer commands.
Therefore to make effective use of FBLOCK for a random block list, you have to load up two block commands before the first FBW event gets triggered. So start with the RDFAST for the first block (with block count of one). Then immediately issue FBLOCK for the second block (also with block count of one). Then enable interrupts, or in the main loop, upon FBW event, issue another FBLOCK (each one having a block count of one).
At time of FBW event, for counts of one, the issued FBLOCK is for a whole block in the future of where the emulator is decoding.
PS: Also, when using non-zero block counts, all start addresses have to be longword aligned.
Although the wrap address could (and should) be on a 64-byte boundary, the RDFAST start address could be anywhere within a 64-byte block. This might be a problem as the block count starts from the RDFAST address.
If required, could the PSRAM code start the streamer before the PSRAM is ready and stream in rubbish data before the desired start address data? This would have to be done only for the RDFAST block.
Only has to be longword aligned. But each block is 64 bytes in size. So, if not all 64 bytes is wanted you still have to read the remainder out of the FIFO before the new block appears.
The alternative is to start again with a fresh RDFAST ... Which maybe a suitable solution because by using a $8000_0000 for the block count it'll fetch in the background and if you've got other things to attend while the FIFO fills then bobs-your-uncle.
And what's more, $8000_0000 is treated as a zero block count. Which means byte alignment is okay to use.
Is this another problem, that rules out automatic wrapping with RDFAST & FBLOCK? On branching, first byte in FIFO must be opcode at exact jump or call address, not up to 3 bytes lower.
I figured, with fixed 64-byte blocks, wasted fetches all round was going to be order of things.
PS: Note, as above, zero count can be byte aligned.