Game of Life on Propeller.
I've been slowly working on a Game of Life solver for a solar powered propeller trinket of mine. The test code attached below runs on any Propeller and displays over the serial port. (112500 Baud) It'll simulate a 96x96 or 128x128 cell world pretty quickly. (showing the life field over the serial port is far slower than the solver)
My solver is based around a 3-bit by 32x parallel adder loop that adds up the number of neighboring live cells. It's pretty quick, in assembly it should only need 2-3 instructions per cell. Does anyone know a faster algorithm suitable for the Propeller and "small" life fields?
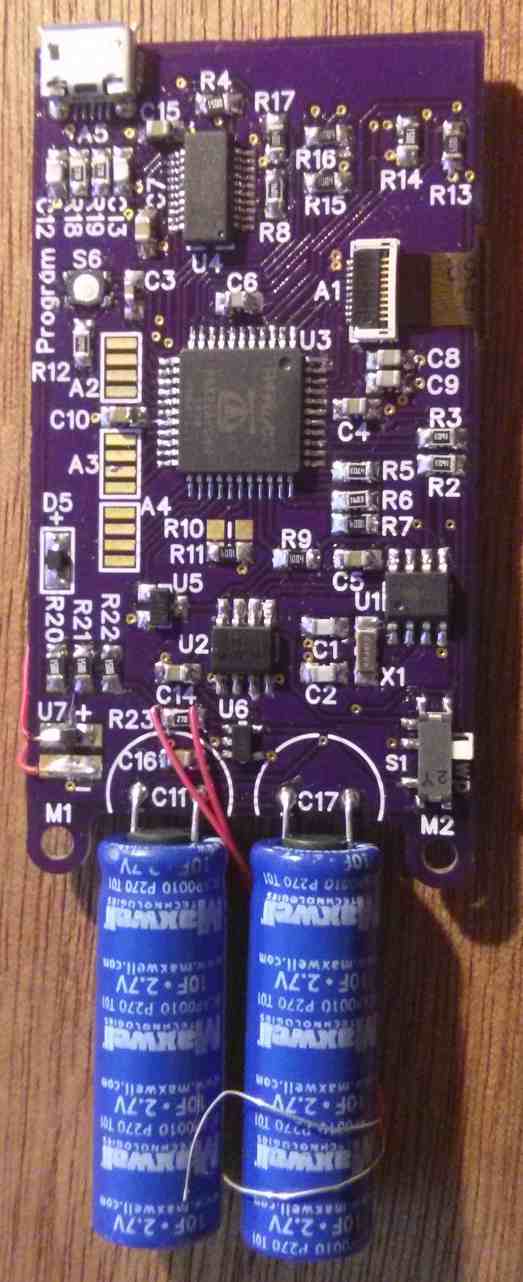
The solar powered trinket in the two pictures always runs on RCSLOW. (the two super-capacitors at the bottom will run it for 6-days on there own) I'd like to calculate the next life generation on less than 10 seconds, so I need to port the life solver to assembly. Right now, the array addressing required is kicking my butt. If someone else wants to take a crack at an assembly Life solver I'd be grateful.
Marty

My solver is based around a 3-bit by 32x parallel adder loop that adds up the number of neighboring live cells. It's pretty quick, in assembly it should only need 2-3 instructions per cell. Does anyone know a faster algorithm suitable for the Propeller and "small" life fields?
The solar powered trinket in the two pictures always runs on RCSLOW. (the two super-capacitors at the bottom will run it for 6-days on there own) I'd like to calculate the next life generation on less than 10 seconds, so I need to port the life solver to assembly. Right now, the array addressing required is kicking my butt. If someone else wants to take a crack at an assembly Life solver I'd be grateful.
Marty





Comments
I commented out some of the unused methods to make it easier for me to see what's going on and I added a few PST commands to make the display look cleaner (to me).
I also changed the initial seed to cnt so the seed value would be different each time the program is run.
I also reduced the size to make it fit better in my PST window.
For some reason this game of life is more mesmerizing than other versions I've seen. It might be because it's kind of slow.
It's a lot of fun to watch. Thanks Lawson.
Edit: I deleted the file attached to this post. There's a better demo of Lawson's code attached to post #7.
Is possible modify this for VGA64 driver ?
Many thanks
Should be. The width of the life field needs to be a multiple of 32 but the life field is just a 2d array of bits. It should directly map to any of the 2-color bit-mapped video drivers. Higher color depth video drivers will need some code to copy the life field to the frame buffer. I expect the spin implementation will run somewhere in the ballpark of 100,000 cells per second. (have not bench marked speed though)
Note: This solver should be able to do other "life like" cellular automata. Say Seeds http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Seeds_%28cellular_automaton%29 or others http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Life-like_cellular_automaton Just have to change the equation at the end of the "col" loop to implement the different rules.
Marty
I assume a comparison of 2D cellular automata solvers exists somewhere on the internet? I'd be really amazed if I stumbled on to an optimal solver in my first try!
I assume Lawson's display is faster than using a serial terminal.
Without the delay the small field transitioned pretty fast. I think the code attached to this post gives a good demonstration of Lawson's algorithm using the Parallax Serial Terminal.
Here's the final output once it's reach an equalibrium state in a recent running of the program.
* ** * * * * * * * ** ** ** * * * * * ** ** * ** ** ** ** * * * * * ** ** ** ** * ** ** * * * * * ** *** * * * * * * * * ** *** ** ** ** ** * * * * * ** ** * * ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** * * * * * * * * * *Using cnt as the seed will create a new system each time the program is run. I've been very surprised how long the program can take to reach an equilibrium point. Some really interesting patterns can emerge as the screen moves toward an equilibrium state.
I really want to try using this on a $5 OLED display.
Doesn't the output to the terminal take about the same amount of time in either Spin or C? What did you time to get 20x faster? The original code had a one second pause in it, I'd think this would be the same in C?
After removed the delay in the main loop, I timed a 96 x 48 array and found about 3/4 of the time was spent writing to the terminal. Only 1/4 of the time was spent updating the array. A loop of the program took about 625ms.
Was it the array updating part which ran 20 times faster?
More progress on my end. I took another crack at conversion to ASM and it looks like it works this time. "memory_lcd_gfx.spin" has the assembly solver. (also includes a "census" call to see how many cells are alive)
Did some benchmarking as well. For a 96x96 (9216 cells) field the SPIN takes 24,113,009 clock cycles while the ASM takes 210,535 clock cycles. Respectively 654 instructions per cell and 5.71 instructions per cell. Looks like the overhead of moving data around is taking as much time as the calculation loop. Also means that I'll need to find 2x more speed or run cores in parallel to meet my 128x128 field in 10 seconds with a 20KHz clock speed goal.
Marty
youtube video
[video=youtube_share;P2hbHXf12Z8]
and at 64 x 24
[video=youtube_share;sSUz2TnHwTs]
TACHYON [~ DECIMAL FORGET LIFE.fth : LIFE.fth ; pub CELLS 2* 2* ; pub 2OVER 4TH 4TH ; 16 == #lines BUFFERS == universe 8 CELLS == bits/cell \ = number of columns pub line ( n -- a-addr ) CELLS universe + ; pub lrot3 ( x1 x2 x3 -- x4 x5 x6 ) 1 ROL ROT 1 ROL ROT 1 ROL ROT ; TABLE #bits 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 3 | pub countbits ( x -- n ) \ count number of bits=1 in bit0..2 7 AND #bits + C@ ; pub alive ( x1 x2 x3 -- flag ) \ return whether cell at bit1 in line1 is alive in next generation OVER 2 AND 0= INVERT >R countbits SWAP countbits + \ note: cell itself is counted, too. correction below. SWAP countbits + DUP 3 = SWAP 4 = R> AND OR ; pub 3dup ( x1 x2 x3 -- x1 x2 x3 x1 x2 x3 ) 3RD 3RD 3RD ; pub doline ( x1 x2 x3 -- x1 x2 x3 x4 ) 0 bits/cell 0 DO >R 3dup alive 2 AND R> OR 1 ROL >R lrot3 R> LOOP ; pub nextgen ( -- ) 0 line @ #lines 1- line @ OVER ( s: line0 x1 x2 ) #lines 1- 0 DO I 1+ line @ ( s: line0 x1 x2 x3 ) doline I line ! ROT DROP ( s: line0 x2 x3 ) LOOP ROT doline #lines 1- line ! \ special treatment for last line 3DROP ; pub .line ( x -- ) bits/cell 0 DO DUP 0< IF "#" ELSE "-" THEN EMIT 1 ROL LOOP DROP ; pub .universe ( -- ) \ print current life state to console #lines 0 DO CR I line @ .line LOOP ; pub life CLS BEGIN HOME .universe nextgen KEY UNTIL ; pub void ( -- ) universe #lines CELLS 0 FILL ; pub seed ( x1 .. xn n -- ) 0 DO i line ! LOOP ; --- some wellknown patterns: pub glider ( -- ) 7 1 2 3 seed ; pub fpent ( -- ) 4 $0C 6 3 seed ; pub lwss ( -- ) $0F #11 1 #12 4 seed ; pub diehard $47 $C0 2 3 seed ; pub acorn $67 8 $20 3 seed ; pub demo glider $700 3 line ! ; ]~ ENDlife2.avi
I did some more optimization yesterday, and with a 128x128 field and a few optimizations, I got the code to just under 5 instructions per cell. (also added a "seed" function to randomly fill the field) I think that's close to the limit for this algorithm without a lot of re-coding.
Looking at Peter's code did give me a new idea. If I compute the partial sum of each cell's neighborhood on each line and shift that partial sum through a pipe-line, I think I can get down to 2.7 instructions per cell. The savings are partly from the more regular buffer shifting patten with fewer line buffers, and partly from eliminating redundant operations while adding up each cell's neighborhood.
Marty
spin2cpp can only produce C/C++ code or binary directly. It's not really designed to translate to ASM, but you could do so by hand (spin2cpp to the C code, then use gcc -S to produce ASM code, then do any fixups necessary to convert from gas to pasm assembly).
Very impressive number on the ASM code! The spin2cpp version (compiled with -Os and the LMM memory model) takes 1,314,112 cycles. If the loops were consolidated it probably wouldn't be hard to use OpenMP to parallelize this.
Eric