Mapping a Rectangle using the Activitybot
Hello. I am trying to have my activitybot use whisker sensors to navigate a rectangle.
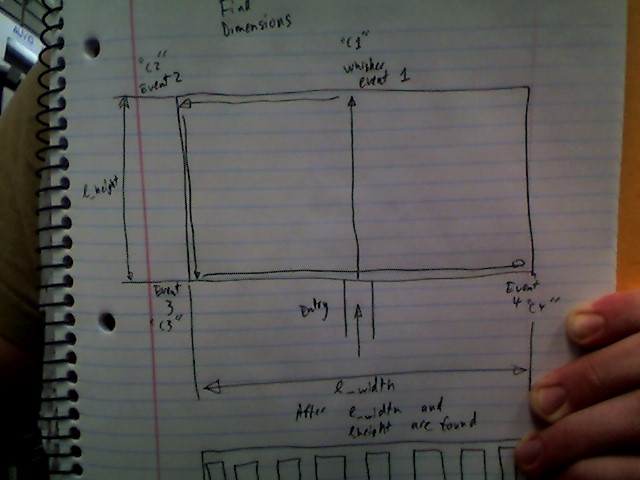
The attached files show the method I would like to use to determine the geometry of the rectangle, followed by the pathing.
At this point, I am working on the pathing code. I've been approaching it as follows:
Move forward until the whisker senses an event. Back up until it can turn left 90 degrees without interference. Travel a variable distance forward, called short_distance. Turn left 90 degrees and go forward l_height distance, or until the whisker is triggered again. (The whisker trigger would be ideal in order to reduce error.) After the second whisker event, it should turn right 90 degrees, travel short_distance and turn right 90 degrees. Then travel forward again either l_height or until another whisker event occurs.
Ideally, we want the travel to end on the bottom left corner so as to allow the bot to travel to the reset point and do the path again.
The attached files show the method I would like to use to determine the geometry of the rectangle, followed by the pathing.
At this point, I am working on the pathing code. I've been approaching it as follows:
Move forward until the whisker senses an event. Back up until it can turn left 90 degrees without interference. Travel a variable distance forward, called short_distance. Turn left 90 degrees and go forward l_height distance, or until the whisker is triggered again. (The whisker trigger would be ideal in order to reduce error.) After the second whisker event, it should turn right 90 degrees, travel short_distance and turn right 90 degrees. Then travel forward again either l_height or until another whisker event occurs.
Ideally, we want the travel to end on the bottom left corner so as to allow the bot to travel to the reset point and do the path again.



Comments
Funny, the STOP command seems to always be the first command i try to perfect...
-Tommy
It is basically a modification of the code used here:
http://learn.parallax.com/activitybot/whisker-wheel-response
I am thinking of taking out the while loop and just having a chain of commands control the bot instead. I believe I may code it as follows:
This will be plain english until I get the language down better.
A counter variable will be set to 0.
If whisker does not recieve input, move forward.
If whisker event occurs, counter = counter + 1, back up, turn left 90 degrees, proceed forward a set distance, left turn 90 degrees.
Ideally, the bot should move forward after this set of functions are complete.
The second whisker event will occur with the following functions resulting:
counter = counter - 1
Turn right 90 degrees, move forward a set distance, turn right 90 degrees.
From here, the bot should move forward again.
outside the initial loop:
if whisker event occurs, total_counter = +1
this will aid the bot in not getting stuck in the far end corner.
It should also allow for the bot to return to the beginning of the mapping (seen in the drawing as the bottom right corner)
This will allow for multiple passes in the same rectangular pattern.
Our main goal is to map a magnetic field in 3 dimensions.
We already have code for a spiral and a straight line.
Eventually, we will add code in which will allow for pauses after a certain distance has been achieved.
We are making a simple gui in Labview to allow users to determine how many measuring spots they can have in a given space.
I can see the potential for using a for loop if we consider each set of left and right turns as one full pass.
You can put an if statement with a break.
If (n == 50) break
The way I'm going to use it is as follows:
Set a distance you want to travel and set n equal to that
http://learn.parallax.com/propeller-c-start-simple/code-repeats
/*
This is the main Rectangular code with drive32 turns and straight program file.
*/
#include "simpletools.h" // Include simple tools
#include "abdrive.h"
#include "math.h"
int main() // Main function
{
// DECLARATION OF VARIABLES
int L_Width_Measured = 600; //Width in millimeters, found from calibration sequence Originally set to 1000 mm
int L_Height_Measured = 200; //Height in millimeters, found from calibration sequence Originally set to 400 mm
int t = 2; //Number of top passes Originally set to 2 passes
int b = t-1; //Number of bottom passes Originally set to 1 passes
float X_Distance = L_Width_Measured/((2*t)-1); //X_Distance traveled; also known as pass distance Originally set to 200 mm
float X_Distance_ticks = X_Distance/3.25; //Ticks traveled for X Distance drive function Originally 6.154mm
float up_and_down = (L_Height_Measured-105.8); //Distance the bot picked up from step (4) in diagram for rectangular pathing
float up_and_down_ticks = up_and_down/3.25; //Ticks traveled for up and down drive function
int n;
int right_turn_pause = 870;
int left_turn_pause = 870;
int increment = 50; //pause increments in mm
float X_Distance_pause_time = (X_Distance_ticks*1000)/(32);
float up_and_down_pause_time = (up_and_down_ticks*1000)/(32);
print(" L_Width_Measured = %d mm\n t = %d passes\n b = %d passes\n X_Distance = %d mm\n X_Distance_ticks = %d ticks \n up_and_down = %d mm \n up_and_down_ticks = %d ticks\n Pause/Sensor Intervals = %d \n", L_Width_Measured, t, b, X_Distance, X_Distance_ticks, up_and_down, up_and_down_ticks, increment);
for(n = 1; n<t; n++) //Repeat t-1 times
{
for ( int i = 0; i<up_and_down; i+=increment)//Go forward up_and_down distance with pause every increment i distance
{
drive_speed(32, 32);
pause(((increment/3.25)/20*1000));
drive_speed(0,0);
pause(500);
}
drive_speed(-32, 32); //90 degrees left turn
pause(left_turn_pause);
drive_speed(0,0);
pause(500);
for (int i = 0; i<X_Distance; i+=increment) //Go forward X_Distance distance with pause every increment i distance
{
drive_speed(32, 32);
pause(((increment/3.25)/20*1000));
drive_speed(0,0);
pause(500);
}
drive_speed(-32, 32); //90 degrees left turn
pause(left_turn_pause);
drive_speed(0,0);
pause(500);
for (int i = 0; i<up_and_down; i+=increment) //Go forward up_and_down distance with pause every increment i distance
{
drive_speed(32, 32);
pause(((increment/3.25)/20*1000));
drive_speed(0,0);
pause(500);
}
drive_speed(32, -32); //90 degrees right turn
pause(right_turn_pause);
drive_speed(0,0);
pause(500);
for (int i = 0; i<X_Distance; i+=increment) //Go forward X_Distance distance with pause every increment i distance
{
drive_speed(32, 32);
pause(((increment/3.25)/20*1000));
drive_speed(0,0);
pause(500);
}
drive_speed(32, -32); //90 degrees right turn
pause(right_turn_pause);
drive_speed(0,0);
pause(500);
print("this is pass n = %d\n", n);
}
// Final Set of Passes
for(n=n; n<=t; n++) //Final set of passes
{
for (int i = 0; i<up_and_down; i+=increment) //Go forward up_and_down distance with pause every increment i distance
{
drive_speed(32, 32);
pause(((increment/3.25)/20*1000));
drive_speed(0,0);
pause(500);
}
drive_speed(-32, 32); //90 degrees left turn
pause(left_turn_pause);
drive_speed(0,0);
pause(500);
for (int i = 0; i<X_Distance; i+=increment) //Go forward X_Distance distance with pause every increment i distance
{
drive_speed(32, 32);
pause(((increment/3.25)/20*1000));
drive_speed(0,0);
pause(500);
}
drive_speed(-32, 32); //90 degrees left turn
pause(left_turn_pause);
drive_speed(0,0);
pause(500);
for (int i = 0; i<up_and_down; i+=increment) //Go forward up_and_down distance with pause every increment i distance
{
drive_speed(32, 32);
pause(((increment/3.25)/20*1000));
drive_speed(0,0);
pause(500);
}
print("the final n value is %d.\n", n);
}
// n = n + 1;
// print("n is now bigger than the loop n = %d\n", n);
}
I've been out of town for a couple of weeks, and missed your post about you learning how to stop your machine, Turns out to be fairly important yes?.
I don't write much code using C, maybe you could 'archive' your code and post that up, so that others could learn from your success.
Congrats again, and keep up the good fun.
-Tommy